Combating Antibiotic Resistance in Africa and Asia: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "{{Project |Description=COVID-19 caused 3.55 million deaths globally in 2021, but antibiotic resistant bacterial infections actually killed 4.95 million people in 2019 - and that number is expected to be 10 million by 2050. Thus we urgently need antibiotic alternatives, particularly in Africa and Asia where 90% of the antibiotic-resistant deaths will occur. Phages for Global Health empowers scientists in Africa and Asia to develop inexpensive, natural antibacterials (phag...") |
(Updated projects) |
||
| (5 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Project | {{Project | ||
|Description= | |Description=Antibiotic-resistant infections are predicted to kill 10 million people each year by 2050 -- five times more than the roughly 2 million deaths caused by COVID-19 in 2020. Thus, we urgently need antibiotic alternatives, particularly in Africa and Asia where 90% of the antibiotic-resistant deaths will occur. Phages for Global Health empowers scientists in Africa and Asia to develop inexpensive, natural antibiotic alternatives (phages) that can kill antibiotic-resistant bacteria. | ||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
=Long-Term Impact= | =Long-Term Impact= | ||
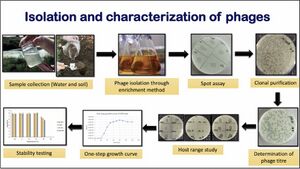
Since 2017 we have delivered 4 in-person workshops in Africa, teaching scientists how to isolate phages. Those trainees have now started >50 phage research projects, won grants totaling to >$945,000, and taught phage biology to 1200 others -- rapid scaling! In 2022 we will run our first virtual workshop, specifically for scientists in Southeast Asia. Since phages can kill antibiotic-resistant bacteria in food, livestock and people, all this work could save thousands of lives, if not millions. | |||
=References= | =References= | ||
# http://phagesforglobalhealth.org/ | # http://phagesforglobalhealth.org/ | ||
# https://www.theguardian.com/global-development/2020/sep/21/phages-the-tiny-viruses-that-could-help-beat-superbugs | # https://www.theguardian.com/global-development/2020/sep/21/phages-the-tiny-viruses-that-could-help-beat-superbugs | ||
# https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KQDiwCyyFII | # https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KQDiwCyyFII | ||
# https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YI3tsmFsrOg | # https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YI3tsmFsrOg | ||
# https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4897794/pdf/fmicb-07-00882.pdf | |||
|Problems= | |||
=Additional Documentation= | |||
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4897794/pdf/fmicb-07-00882.pdf | |||
=Project Gallery= | |||
|Problems=205024,203779 | |||
|Solutions=203781 | |||
|organization_id=133410 | |organization_id=133410 | ||
|Region=Malaysia | |Region=Malaysia | ||
|Resources=['http://phagesforglobalhealth.org/ | |Resources=['http://phagesforglobalhealth.org/', 'https://www.theguardian.com/global-development/2020/sep/21/phages-the-tiny-viruses-that-could-help-beat-superbugs', 'https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KQDiwCyyFII', 'https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YI3tsmFsrOg', 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4897794/pdf/fmicb-07-00882.pdf'] | ||
|scraped_url=https://www.globalgiving.org/projects/combating-antibiotic-resistance-in-africa-and-asia | |scraped_url=https://www.globalgiving.org/projects/combating-antibiotic-resistance-in-africa-and-asia/ | ||
|scraped_from=GlobalGiving | |scraped_from=GlobalGiving | ||
|feature_image=File: | |feature_image=File:Heera_lecture_phage_characterization_Large.jpg|Some topics covered during the workshop | ||
|images=[[File: | |images=[[File:ph_54735_213842.jpg|,File:ph_54735_213843.jpg|,File:Tobi_announcing_phage_bank_meeting_CROPPED_2_Large.jpg|Tobi at the Viruses of Microbes conference,File:Final_session_everyone_names_removed_Large.jpg|Final session of the phage workshop,]] | ||
|coordinate=, | |coordinate=, | ||
|geo_id=1733045}} | |geo_id=1733045}} | ||
Latest revision as of 11:35, 5 August 2023
| Organization | Phages for Global Health |
|---|---|
| Region | Malaysia |
| Website | Website |
| N/A | |
| N/A | |
| ProjectLeader | Tobi Nagel |
| Linked Problems & Solutions
|
|---|
Antibiotic-resistant infections are predicted to kill 10 million people each year by 2050 -- five times more than the roughly 2 million deaths caused by COVID-19 in 2020. Thus, we urgently need antibiotic alternatives, particularly in Africa and Asia where 90% of the antibiotic-resistant deaths will occur. Phages for Global Health empowers scientists in Africa and Asia to develop inexpensive, natural antibiotic alternatives (phages) that can kill antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
Challenge
The antibiotic resistance crisis disproportionately impacts developing countries, and misuse of antibiotics in COVID-19 patients is expected to increase antibiotic resistance rates worldwide. Before antibiotics were discovered, phages were used as antibacterial agents. With few other treatment options available now, phage-based drugs are regaining popularity in industrialized nations, but most researchers in developing countries lack the expertise to develop and utilize them effectively.
Long-Term Impact
Since 2017 we have delivered 4 in-person workshops in Africa, teaching scientists how to isolate phages. Those trainees have now started >50 phage research projects, won grants totaling to >$945,000, and taught phage biology to 1200 others -- rapid scaling! In 2022 we will run our first virtual workshop, specifically for scientists in Southeast Asia. Since phages can kill antibiotic-resistant bacteria in food, livestock and people, all this work could save thousands of lives, if not millions.
References
- http://phagesforglobalhealth.org/
- https://www.theguardian.com/global-development/2020/sep/21/phages-the-tiny-viruses-that-could-help-beat-superbugs
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KQDiwCyyFII
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YI3tsmFsrOg
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4897794/pdf/fmicb-07-00882.pdf
Additional Documentation
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4897794/pdf/fmicb-07-00882.pdf
Project Gallery